pp. 15 & 16
Cope Rearrangement (Very similar to the Diels-Alder Reaction)
The Cope rearrangement was discovered by Arthur C. Cope and is a thermal isomerization reaction of a 1,5-diene. A general Cope reaction is shown below:
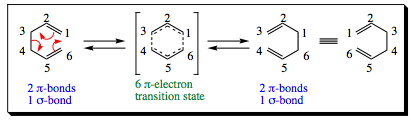
In this reaction, the bonds rearrange to break and reform both pi-bonds and sigma-bonds, resulting in a true skeletal rearrangement. This reaction, just as the Diels-Alder, goes through a transition state that has 6 electrons interacting in a cyclic, delocalized sense. As with the Diels-Alder reaction, the transition state is considered aromatic when the reaction is concerted (all bonds broken and made at the same time). There are some Cope rearrangements that go through more of a diradical intermediate, but we are not going to focus on that pathway at this time.
Show below is an orbital view of a Cope rearrangement reaction:
- Orbital View of this Reaction:
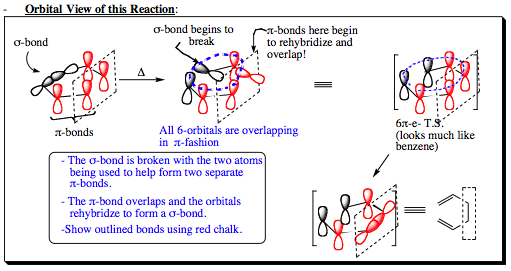
The movie below may more fully articulate the mechanism and orbital interactions in a Cope rearrangement:
(For a larger version of this movie, please click HERE)
| PREVIOUS PAGE (13 & 14) | Back to Index | NEXT PAGE (17 & 18) |