Problem Set Chapter 4
Organic Chemistry
1. The following values have been observed.
i) The l max for ethene is 176 nm.
ii) The l max for 1,3-butadiene is 217 nm.
iii) The l max for 1,5-hexadiene is 184 nm.
a) Use an MO diagram to show the p-p* transition for ethene.
b) Use an MO diagram to show the p-p* transition for 1,3-butadiene.
c) Why is the lmax of 1,5-hexadiene closer to that of ethene than 1,3-butadiene.
2. Three compounds A, B, and C, have the same molecular formula (C5H6). In the presence of a platinum catalyst, all three
compounds absorb 3 molar equivalents of hydrogen and yield pentane. Compounds A and B both contain an acidic proton,
but C does not. Compounds A and C show an absorption maximum near 230 nm while compound B shows no
absorption maximum above 200 nm. Propose structures for compounds A, B, and C.
3. a) Draw an MO diagram for the a,b-unsaturated aldehyde CH3-CH=CH-CH=O
b) Use your MO diagram to show a p-p* transition.
c) Use your diagram to show an n-p* transition.
d) Comment on the relative energy of these two transitions.
4. Two compounds have the same molecular formula (C5H8O). Both show a UV absorption maximum at 230 nm. Compound A
also shows an absorption at 279 nm while B does not. Reaction with 1 eq. of H2/Pt with each compound results in the
disappearance of the absorption maximum at 230 nmin both compounds, although A retains its absorption maximum at 279 nm.
Reaction with a second eq. of H2/Pt is possible with both compounds and results in the loss of the 279 absorption maximum for
compound A. Propose structures for compounds A and B.
5. Draw the structure correlating the molecular formula with the 1H NMR for the following compounds.
a.

b.

c. Molecule contains one ring.

6. Identify the two isomers 1,3-dibromo-1,3-dimethylcyclobutanes on the basis of their 1H NMR data:
Isomer One Isomer Two
singlet d 2.13, 6H singlet d 1.88, 6H
singlet d 3.21, 4H doublet, d 2.84, 2H
doublet, d 3.54, 2H
7. Two compounds, A and B, have the same molecular formula (C6H8). Both compounds react with 2 molar equivalents of H2
in the presence of platinum to yield cyclohexane as shown below.
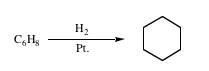
Compound A: Shows absorption max in the UV at 256 nm.
Shows 3 peaks in the 1H NMR.
Compound B: Shows no absorption max in the UV above 200 nm.
Shows 2 peaks in the 1H NMR.
What are the structures of A and B.
8. Compounds A and B both have a molecular structure of C8H8O3. Catalytic hydrogenation of both A and B leads to C.
Spectral data for compounds A, B, and C are summarized below. Assign structures for compounds A, B, and C and explain
your reasoning.

9. When dissolved in CDCl3, a compound (K) with the molecular formula C4H8O2 gives a 1H NMR spectrum that consists
of a doublet at d 1.35, a singlet at d 2.15, and broad singlet at d 3.75 (1H), and a quartet at d 4.25 (1 H). When dissolved in
D2O, the compound gives a similar 1H NMR spectrum, with the exception that the signal at d 3.75 has disappeared.
The IR spectrum of the compound shows a strong absorption peak near 1720 cm-1.
a. Propose a structure for compound K and
b. Explain why the NMR signal at d 3.75 disappears when D2O is used as the solvent.
10. For the following molecules, provide
(a) UV transitions and approximate wavelengths (if any)
(b) identity and molecular weight of parent ion (M+)
(c) the expected major absorbances in the IR spectrum
(d) the number of anticipated 13C NMR resonances
(e) a sketch of the anticipated 1H NMR spectrum
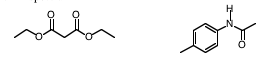
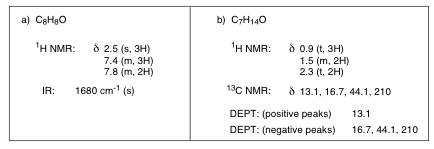
11. Propose a structure from the following spectral data:
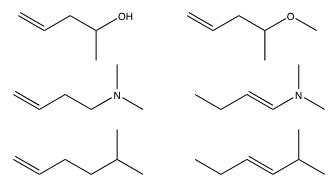
12. For the following molecules, draw the 1H NMR spectrum you would expect to see. Include any expected multiplicities and
approximate chemical shifts. How many 13C NMR peaks do you expect?
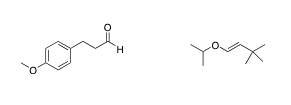
13. Given the following spectroscopic information, what is the structure of the compound?

14. In the following examples, draw out the expected proton and carbon NMR along with the expected UV and IR spectra.
Give the expected m/z of the parent ion and major fragments, showing with arrow flow how the molecule would fragment.